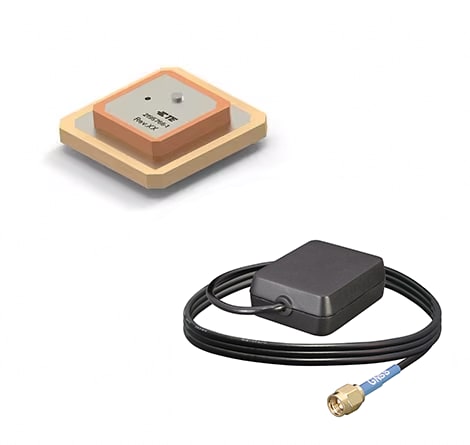

GNSS Antennas & GPS Antennas: Multi-band antennas for individual device configuration
TE Connectivity's (TE) GNSS (global navigation satellite system) antennas comprise all common global satellite services such as GPS, GALILEO and BeiDou. Our GNSS antennas and GPS antennas are suited for use in the area of public security, in the transport and logistics sectors as well as for protection against theft and in industrial applications. Equipped with powerful, low-profile antennas, most of the systems can be tailored to your needs – from cables and connectors to rugged housing.
Our portfolio includes GNSS antennas & GPS antennas that can be used in combination with mobile communication antennas to provide telematic services such as eCall or vehicle tracking system (VTS). The dominate technology for GNSS reception is the use of ceramic patch antennas that have a very low profile. Due to the weak signal of GNSS, a low noise amplifier is typically part of our antenna design.
Standard Portfolio
Readily available for design-in
Our new standard portfolio of GNSS antennas makes positioning wireless connections more reliable by using a range of multi-band antennas for individual device configuration. With the 5G rollout and exponential increase of wireless traffic, quality of service and spectral efficiency are becoming more and more critical for a non-interrupted wireless experience. Our new standard portfolio addresses key antenna performance goals – efficiency and bandwidth – and covers different requirements, from generic consumer navigation to high precision positioning.
Key Benefits:
- Enhance efficiency and bandwidth
- Reduce antenna size
- Save costs with minimum associated components required
- Support multi-band/multi-standard


GNSS & GPS Antennas
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What performance and precision level should I consider when choosing a GNSS antenna?
A: GNSS antennas can operate in one or multiple bands, including GPS, BeiDou and GALILEO. The more bands used simultaneously, the better the position can be determined. Antenna performance is largely constrained by the laws of physics - the physical aspects of an antenna play an important role in its performance parameters. When making your decision, it’s worth considering if the GNSS antenna will be receiving signals in free space or will be used in blocked areas like downtown in larger cities.
Q: Will the size of my application/device and other design aspects and use cases affect the performance of a GNSS antenna?
A: The size of a device and it’s ground plane can have a major impact on an antenna’s RF performance. Oftentimes, the device becomes part of the antenna and the position and orientation of other components within the device will affect the antenna’s ability to send and receive signal. In addition, the device might not be always directed towards the sky but must operate in various and random orientations. In this case, it’s worth looking for a more spherical omnidirectional antenna.
Q: Do I need an internal or external GNSS antenna?
A: Some devices may not allow you to use an internal GNSS antenna for various reasons such as internal interference with other components, limited space, or usage a blocked location. In this case, an external GNSS antenna would be needed, connected to the device by a coax cable and an RF connector.




